FEGate for Ship
Pre/Post Processor for Shipbuilding Industry
Model Check
Verify key structural properties and create reliable reports.
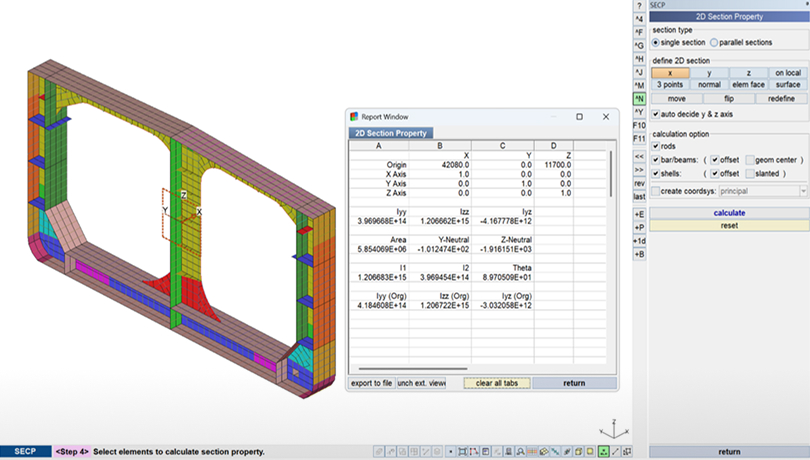

Section Property
Computes moment of inertia, area, and neutral axis of composite sections combining shell and 1D stiffeners.
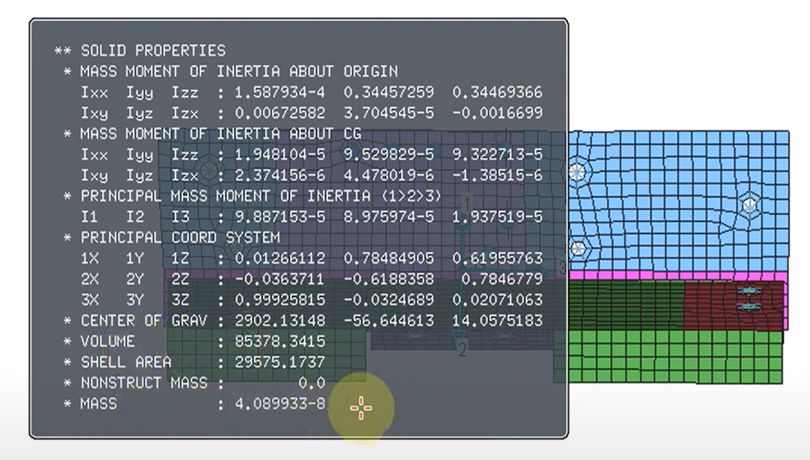

Solid Property
Calculates and displays mass, volume, center of gravity, mass moment of inertia, and principal axes for selected shell and 1D elements (with optional report file output).
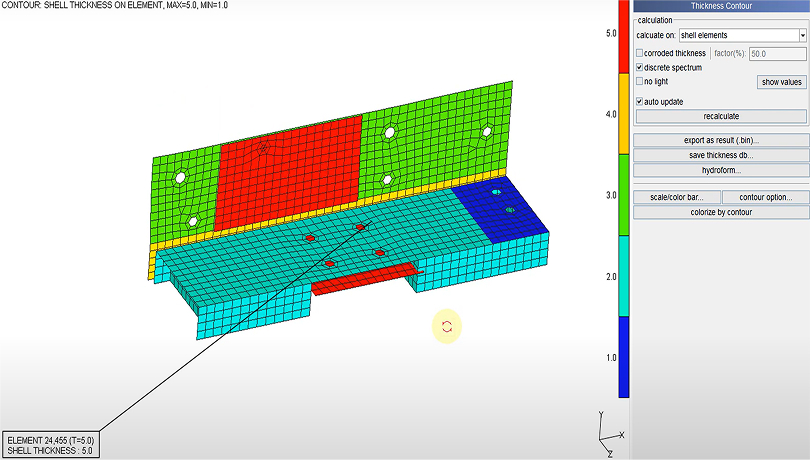

Thickness Contour
Visualizes thickness distribution using thickness values defined in shell properties and vertex nodes.
Post Processing
Combine and visualize results for faster decision-making.
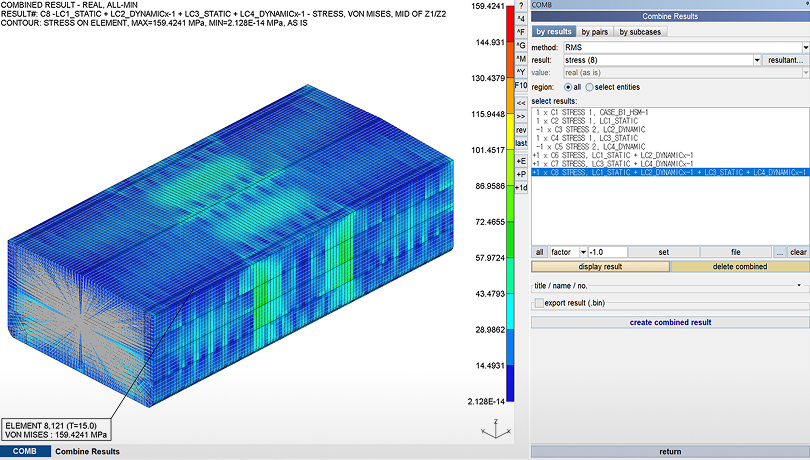

Combine Result
Generates new stress or displacement results by statistically combining multiple load case results.
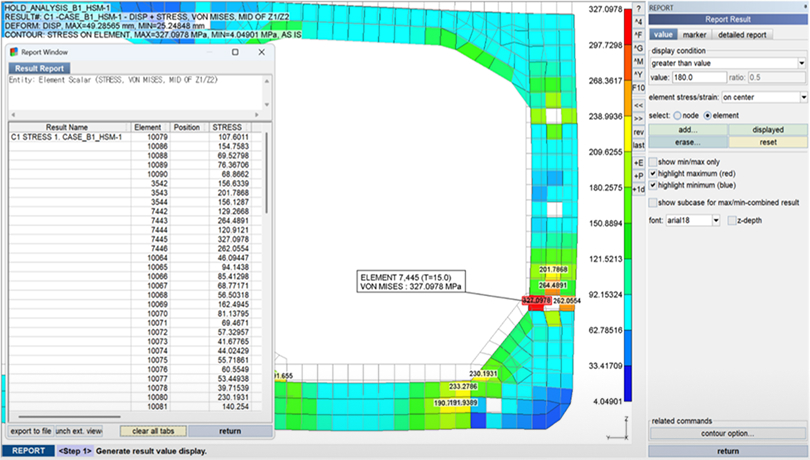

Report
Displays results as text annotations on the FE model and outputs scalar or tensor values in tabular format.
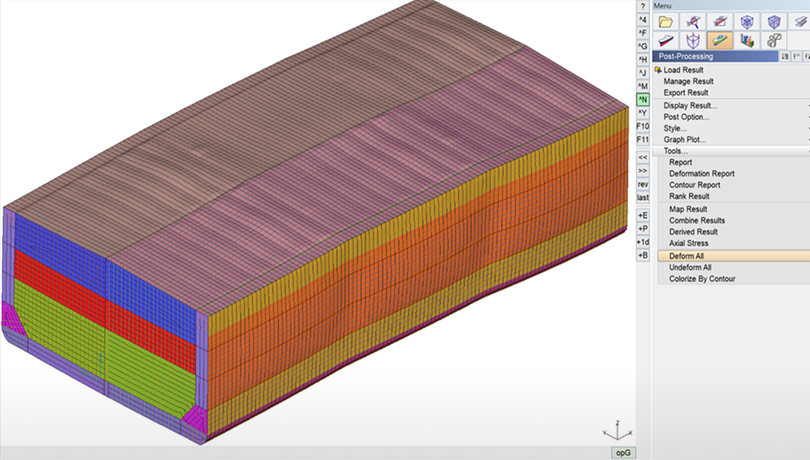

Deform All
Deforms the FE model geometry by applying the currently displayed deformation results to node positions.
Property Edit
Modify mass, beam properties, and apply corrosion adjustments.
Load Conversion
Convert and map complex loads with ease.


Pressure ↔ Force
Supports bidirectional conversion between element pressure loads and equivalent nodal forces.


Gravity → Force
Applies equivalent nodal forces by reflecting gravity based on density, area, and other properties defined for selected entities.
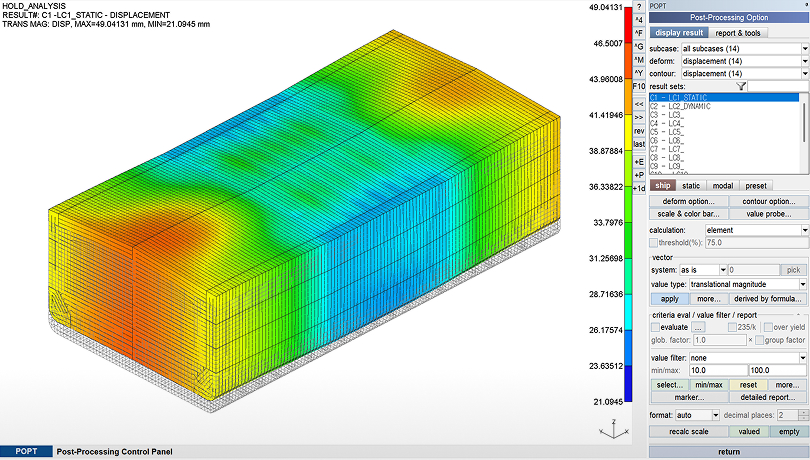

Result → BC
Applies deformation results as enforced displacement boundary conditions or converts reaction forces into external loads.
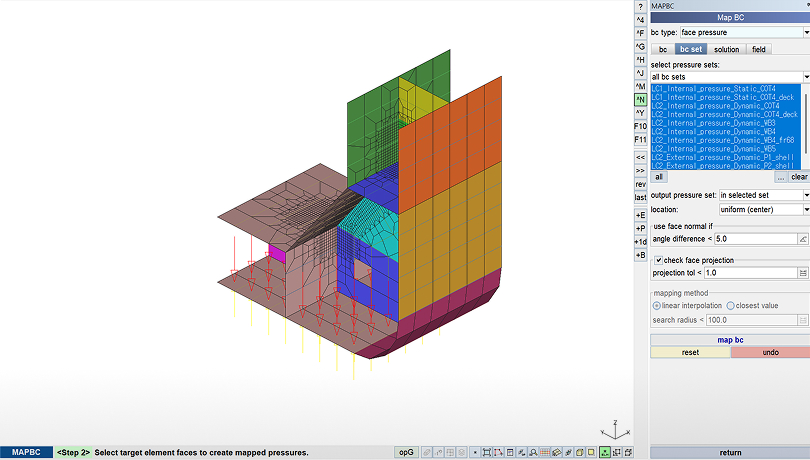

Map BC
Maps boundary conditions from a global model onto a submodel for consistent local analysis.
S/W Development &
Automation
Enhance efficiency using APIs and automation tools.
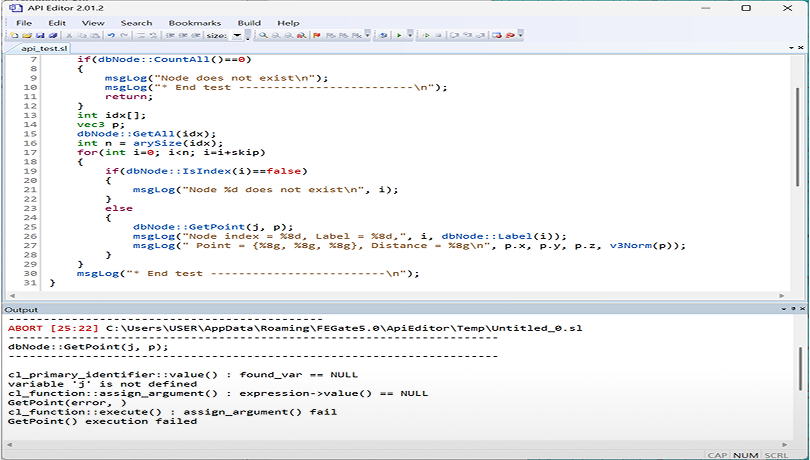

API
Enables users to implement custom functions within FEGate and easily identify code errors through the built-in API Editor.


Script & Script builder
Automatically generates FEGate-recognizable scripts for loads and boundary conditions by simply inputting node IDs and values in a table format.

Specialized Solver,
RAPIDUS
Perform large-scale linear analysis with fast parallel computing.
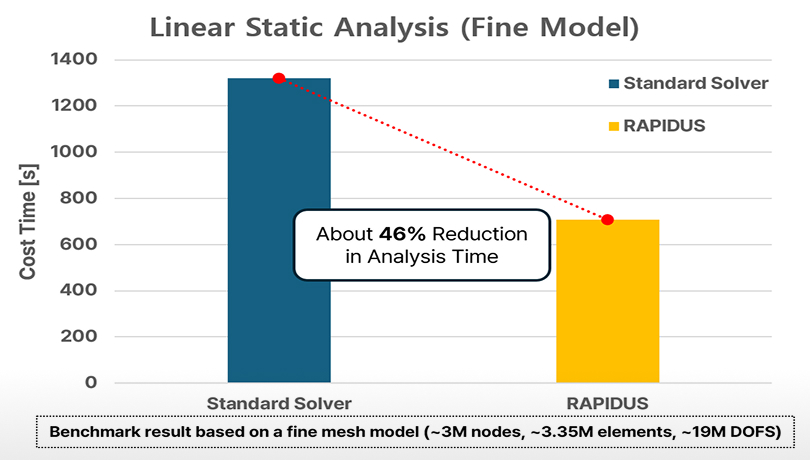

Rapid Linear Analysis Performance
RAPIDUS significantly accelerates linear static analysis, especially in high-DOF models, as shown in benchmark tests with over 19 million DOFs.
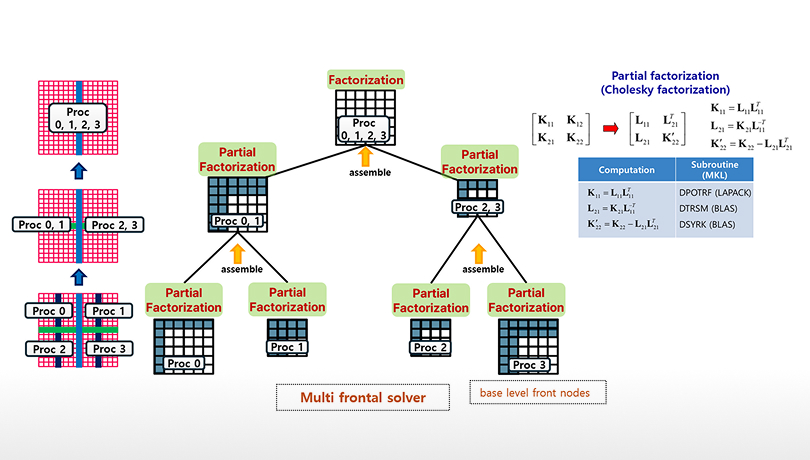

High Performance in Parallel Computing Capabilities
Provides high-performance parallel computation through various solver types including MFS, Dense, Sparse, and AMG (figure shows MFS parallelization).