BLOG
Hello, this is RaonX Solutions Co., Ltd.
This time, we would like to share a usage tip for FEGate for Ship,
specifically regarding the Transform 2D → 3D (Command: TR3D) feature.
In shipyard operations, when modeling hull structures,
there are often situations where you need a feature to easily position 2D-defined shapes in 3D space.
FEGate for Ship (FFS) addresses this need by providing the TR3D (Transform 2D → 3D) feature,
which converts 2D geometry to the desired 3D location.
Access Method
Feature Overview
TR3D is a tool that allows you to rotate and move existing 2D shapes based on a selected plane, enabling placement in a user-defined 3D space.
Using this feature, you can easily perform tasks such as (see Figure 1):
- Positioning shapes in Cross-section (X-Sect), Longitudinal (Y-Elev), and Plan (Z-Plan) views
- Creating symmetrical shapes through Rear View transformation
- Conveniently moving models by entering coordinate values or selecting reference nodes
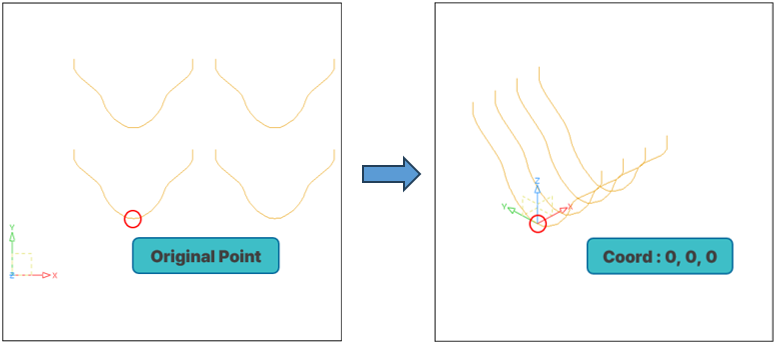
Figure 1. TR3D Transformation Result of Imported Geometry
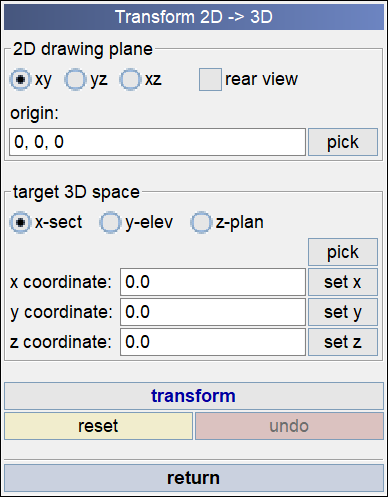
Figure 1.Transform 2D → 3D (General)
Key Feature Description
TR3D is a tool that allows you to rotate and move existing 2D shapes based on a selected plane, enabling placement in a user-defined 3D space.
Using this feature, you can easily perform tasks such as (see Figure 1):
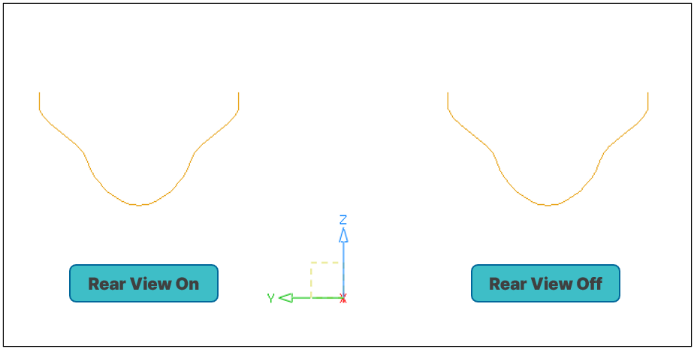
Figure 3. Effect of Rear View Option (Target Space : X-Sect)
Target 3D Space :
Usage Steps
1. Select 2D Geometry
Choose the geometry you want to move.
2. Set 2D Drawing Plane and Target 3D Space
Specify the plane on which the selected geometry is located and the target plane for final placement.
For example, if the geometry is on the XY plane and you want a cross-sectional placement, set the Target to X-Sect.
3. Select Origin or Enter Coordinates
Pick the reference point on the geometry or manually enter the X, Y, Z coordinates.
This point becomes the center of the transformation.
4. Specify Target Location – Use FE Model Nodes
Click the Pick button in the Target 3D Space section to select a specific node on the FE model.
The selected node’s coordinates are automatically imported, preparing the reference point to move to this position.
5. Click Transform Button or MMB (Middle Mouse Button)
Execute the transformation to move and rotate the geometry into the 3D space.
Tips for Use
Feature Example
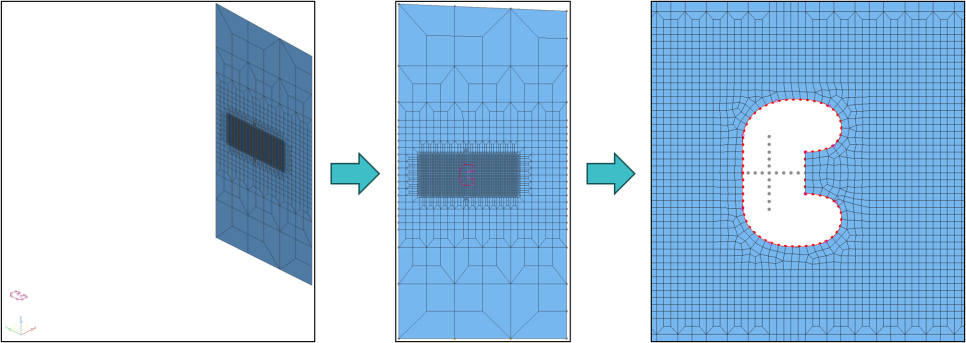
Figure 4. Using TR3D to Insert Imported Geometry and Modify FE Model
This is an example of creating holes (Cutouts) in an FE model based on a 2D shape imported from an external source (e.g., IGES file) after precisely placing it in the desired position using the TR3D feature.
By aligning the shape to a specific plane in 3D space with TR3D, and then modifying the mesh along the imported geometry, structural features can be effectively processed.
The TR3D feature is particularly useful for complex FE geometry modifications or model editing based on CAD-derived shapes.
This concludes the overview of the Transform 2D → 3D feature.
If you have any further questions, please contact us at support@raonx.com.


